How to Plan the Perfect Time to Plant Grass Seed for a Full Lawn is a crucial step in achieving a lush, vibrant lawn. The success of your grass seed depends heavily on the timing of planting, which is dictated by the ideal soil temperature for germination.
Understanding the ideal planting window for your region and grass type is essential for maximizing your chances of a successful lawn.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of planning the perfect time to plant grass seed, covering everything from soil preparation to choosing the right grass seed mix. We’ll also explore the importance of consistent watering and protecting your new lawn from pests and diseases.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to a thriving, beautiful lawn that you can enjoy for years to come.
Understanding Grass Seed Timing
Planting grass seed at the right time is crucial for successful lawn establishment. Understanding the ideal timing depends on factors like soil temperature and regional climate.
Soil Temperature and Grass Seed Germination
Soil temperature plays a vital role in grass seed germination. When the soil reaches the optimal temperature range for a particular grass type, the seeds begin to sprout. However, if the soil is too cold, the seeds may remain dormant.
While planning the perfect time to plant grass seed for a full lawn, consider the benefits of fall planting. The cooler temperatures and consistent moisture create ideal conditions for successful germination. And if you have limited space, check out Fall Gardening For Small Spaces: What You Can Grow for inspiration on maximizing your garden.
Once you’ve established a healthy lawn, you can then focus on the seasonal beauty of your flowerbeds and vegetable patches.
Conversely, if the soil is too hot, the seeds may be damaged or fail to germinate.
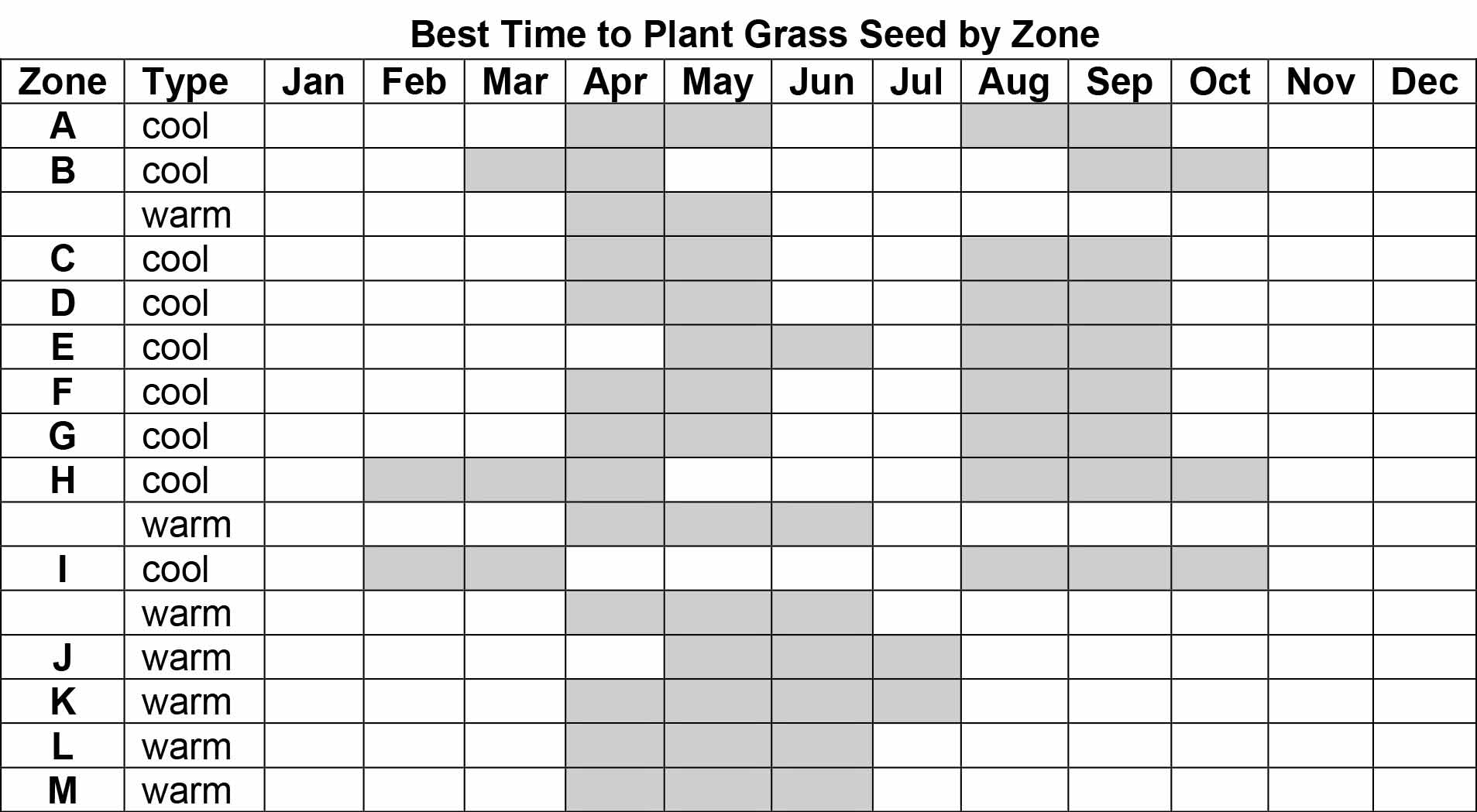
Ideal Soil Temperature Ranges for Different Grass Types
- Cool-Season Grasses:These grasses thrive in cooler temperatures and prefer soil temperatures between 50°F and 70°F (10°C and 21°C). Examples include Kentucky bluegrass, perennial ryegrass, and fine fescue.
- Warm-Season Grasses:These grasses are best suited for warmer climates and germinate well in soil temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C and 29°C). Examples include Bermuda grass, zoysia grass, and St. Augustine grass.
Planting Windows for Various Regions
- Northern Regions:In areas with cold winters, the best time to plant cool-season grasses is in the early fall, usually between late August and mid-September. This allows the grass to establish roots before the ground freezes.
- Southern Regions:In warmer climates, the ideal time to plant cool-season grasses is in the early spring, typically between late February and early April. This allows the grass to take advantage of cooler temperatures and adequate moisture.
- Warm-Season Grasses:These grasses are typically planted in the late spring or early summer, depending on the specific region. For example, Bermuda grass is often planted in late spring or early summer, while zoysia grass may be planted later in the summer.
Preparing the Soil: How To Plan The Perfect Time To Plant Grass Seed For A Full Lawn
A healthy lawn starts with healthy soil. Before you can sow your grass seed, you need to prepare the soil by removing weeds, debris, and thatch, and then aerating and amending the soil.
Removing Weeds, Debris, and Thatch
These are crucial steps in preparing your soil for new grass.
- Weeds:Weeds compete with your new grass for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Removing them before planting is essential. You can pull them by hand, use a weed killer, or a combination of both methods.
- Debris:Any debris, such as leaves, twigs, or rocks, can hinder grass seed germination and growth. Rake or remove them to create a smooth surface for planting.
- Thatch:Thatch is a layer of dead grass, roots, and other organic matter that builds up on the soil surface. It can prevent water and nutrients from reaching the soil and roots, making it difficult for new grass to establish. You can remove thatch with a dethatching rake or by hiring a professional service.
Aerating the Soil
Aerating the soil involves creating small holes in the soil to improve drainage, air circulation, and root growth. This is especially important if your soil is compacted.
- Benefits of Aeration:Aeration allows water and nutrients to penetrate the soil more easily, reduces soil compaction, and promotes healthy root growth.
- Methods of Aeration:You can aerate your lawn using a manual aerator, a gas-powered aerator, or by hiring a professional service.
Adding Amendments
Amendments are materials that are added to the soil to improve its texture, fertility, and drainage.
- Compost:Compost is a great amendment for lawns as it improves soil structure, adds nutrients, and helps retain moisture.
- Topsoil:Topsoil is the top layer of soil and is rich in nutrients. Adding topsoil can improve the fertility of your lawn and provide a good base for new grass to grow.
- Lime:Lime is used to raise the pH of acidic soils. Testing your soil pH is essential to determine if you need to add lime.
Choosing the Right Grass Seed
Selecting the right grass seed is crucial for achieving a healthy, thriving lawn. The type of grass you choose will determine its appearance, growth habits, and ability to withstand environmental conditions. Factors such as your climate, soil type, and desired lawn usage will all influence your choice.
Comparing Different Grass Types, How to Plan the Perfect Time to Plant Grass Seed for a Full Lawn
Different grass types possess unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific environments and purposes. Understanding these differences will help you choose the best seed for your lawn.
Grass Type |
Shade Tolerance |
Drought Resistance |
Foot Traffic Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
Kentucky Bluegrass |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Good |
Perennial Ryegrass |
Low |
Moderate |
Excellent |
Fine Fescue |
High |
Moderate |
Good |
Zoysia Grass |
Moderate |
High |
Excellent |
Bermuda Grass |
Low |
High |
Excellent |
Selecting the Appropriate Grass Seed Mix
For most lawns, a blend of different grass types is recommended. This creates a more resilient and adaptable lawn. Consider the following factors when choosing a seed mix:
- Climate:Cool-season grasses thrive in cooler climates, while warm-season grasses are best suited for warmer regions.
- Sunlight:Some grasses tolerate shade better than others. If your lawn receives limited sunlight, choose a shade-tolerant mix.
- Foot Traffic:If your lawn receives heavy foot traffic, select a mix that is known for its durability.
- Soil Type:Certain grasses prefer specific soil conditions. Choose a mix that is compatible with your soil type.
Pros and Cons of Warm-Season and Cool-Season Grasses
Warm-season and cool-season grasses are the two main categories of lawn grasses. Understanding their differences can help you choose the best option for your climate.
Warm-Season Grasses
- Pros:
- Excellent drought resistance
- High heat tolerance
- Generally require less mowing
- Cons:
- Go dormant in cooler months
- May require more fertilization
- Not suitable for all climates
Cool-Season Grasses
- Pros:
- Thrive in cooler temperatures
- Generally easier to establish
- Widely available
- Cons:
- May go dormant in hot weather
- Require more watering during dry periods
- May need more frequent mowing
Planting the Grass Seed
Planting grass seed is a crucial step in establishing a lush, healthy lawn. The success of your lawn depends on spreading the seed evenly and at the appropriate rate. This ensures that every part of your lawn receives adequate coverage and has a chance to grow.
Methods for Spreading Grass Seed
There are several methods for spreading grass seed, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Broadcasting: This method involves simply scattering the seed by hand over the prepared soil. It is the simplest and most affordable method, but it can be difficult to achieve even coverage, especially on larger lawns.
- Overseeding: This method involves spreading grass seed over an existing lawn. It is a great way to thicken up a thin lawn or introduce new varieties of grass. Overseeding is typically done in the fall or spring when the existing grass is dormant or actively growing.
- Seed Spreader: Using a seed spreader is the most efficient and accurate method for spreading grass seed. Seed spreaders come in various sizes and styles, from manual push spreaders to motorized models. They allow you to distribute the seed evenly and at the recommended rate, ensuring consistent coverage.
Visual Guide
Broadcasting:Imagine scattering a handful of seed across a prepared soil area. You are manually throwing the seed, aiming for even distribution, but this can be challenging to achieve. Overseeding:Visualize scattering seed over an existing lawn. The seed is applied over the existing grass, with the goal of filling in bare spots and thickening the lawn.
Seed Spreader:Imagine a device that distributes seed in a controlled manner, with adjustable settings to control the spread rate. The seed is evenly dispersed, resulting in a consistent coverage of the lawn.
Timing is crucial for a lush, healthy lawn, and the best time to plant grass seed often aligns with the cooler temperatures of fall. While you’re focusing on your lawn, you can also take advantage of the season’s ideal growing conditions for a bountiful harvest by planting vegetables.
How To Grow Nutritious Vegetables In The Fall provides a comprehensive guide to fall vegetable gardening, helping you cultivate delicious and nutritious produce while your lawn takes root. After a successful fall garden, you’ll be ready to enjoy the fruits of your labor and a thriving lawn in the coming spring.
Recommended Seeding Rates
The recommended seeding rate for different types of grass varies depending on the type of seed, soil conditions, and climate. Here is a table outlining the recommended seeding rates for various grass types:
Grass Type |
Seeding Rate (lbs/1000 sq ft) |
|---|---|
Kentucky Bluegrass |
3-5 |
Perennial Ryegrass |
4-6 |
Fine Fescue |
2-3 |
Tall Fescue |
3-4 |
Zoysia Grass |
1-2 |
Bermuda Grass |
2-3 |
It is important to note that these are just general guidelines. The actual seeding rate may vary depending on the specific conditions of your lawn. It is always best to consult with a local landscaping professional for personalized advice.
Watering and Maintaining the New Lawn
Watering your new lawn is crucial for successful germination and establishment. Consistent and adequate moisture allows the grass seeds to sprout, develop roots, and thrive. Without proper watering, the seeds may not germinate, or the seedlings may become weak and susceptible to disease.
Watering Schedule for the First Few Weeks
A consistent watering schedule is vital for the first few weeks after planting grass seed. The goal is to keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Here is a recommended watering schedule for the first few weeks after planting:
- Week 1:Water twice daily, for short durations, to ensure the soil stays moist. This will help the seeds germinate and establish roots.
- Week 2:Gradually reduce watering to once a day. The seedlings will be developing roots and need less frequent watering.
- Week 3:Water every other day, or when the top inch of soil feels dry. The grass should be starting to grow and will need less frequent watering.
- Week 4:Water every two to three days, or when the top inch of soil feels dry. The grass should be well-established and can tolerate slightly drier conditions.
Preventing the New Lawn from Drying Out or Becoming Waterlogged
Overwatering can lead to root rot and fungal diseases, while underwatering can stunt growth and make the lawn susceptible to drought stress. Here are some tips for preventing these issues:
- Water deeply and infrequently:It’s better to water deeply once or twice a week than to water shallowly every day. Deep watering encourages roots to grow deeper, making the lawn more drought-tolerant.
- Monitor soil moisture:Use a moisture meter or stick your finger into the soil to check the moisture level. If the top inch of soil is dry, it’s time to water.
- Avoid watering during the hottest part of the day:Watering in the morning or evening is best, as it minimizes evaporation and allows the water to penetrate the soil more effectively.
- Use a sprinkler system:A sprinkler system can help ensure even watering and prevent overwatering or underwatering. Choose a system that delivers water evenly across the lawn.
Protecting the New Lawn
Your hard work in planting grass seed will be wasted if you don’t protect your new lawn from pests and diseases. These threats can damage your lawn, leaving it weak, patchy, and unsightly. It’s crucial to take proactive measures to safeguard your investment and enjoy a lush, healthy lawn.
Common Lawn Pests and Diseases
Identifying common lawn pests and diseases is the first step in protecting your new lawn. Early detection and treatment are crucial to preventing significant damage.
- Grubs: These beetle larvae feed on grass roots, causing brown patches and making the lawn feel spongy. Signs include birds digging in the lawn and uneven patches.
- Chinch Bugs: These small insects suck sap from grass blades, creating brown, straw-like patches. They are most active in hot, dry weather.
- White Grubs: Similar to grubs, these larvae feed on grass roots, causing damage that can be mistaken for drought stress. They are often found in lawns with a history of poor drainage.
- Dollar Spot: This fungal disease creates small, circular patches of brown, dead grass that resemble dollar coins. It thrives in humid conditions.
- Brown Patch: Another fungal disease, brown patch creates large, irregular patches of brown, dead grass. It’s common in hot, humid weather.
Controlling Pests and Diseases
- Cultural Practices: Healthy lawns are more resistant to pests and diseases. Regular mowing at the proper height, proper fertilization, and adequate watering contribute to a strong lawn.
- Chemical Control: Insecticides and fungicides are effective for controlling pests and diseases. Always follow label instructions carefully and apply products when necessary.
- Natural Control Methods: Using natural pest control methods can minimize chemical usage.
- Beneficial Insects: Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings that prey on pests.
- Neem Oil: This natural oil acts as an insecticide and fungicide.
- Diatomaceous Earth: This powder made from fossilized algae is effective against a variety of insects.
- Organic Fungicides: Use products containing copper or sulfur to control fungal diseases.
Closure
Planting grass seed at the optimal time is the foundation for a healthy and thriving lawn. By understanding the ideal soil temperature, preparing the soil properly, selecting the right grass seed mix, and following proper watering and maintenance practices, you’ll set yourself up for success.
Remember, patience and consistent care are key to nurturing a beautiful lawn. With a little planning and effort, you can enjoy the rewards of a lush, green oasis in your own backyard.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I plant grass seed too early?
Planting grass seed too early in the season, before the soil has warmed sufficiently, can lead to slow or uneven germination, and the seeds may be susceptible to fungal diseases.
What if I plant grass seed too late in the season?
Planting grass seed too late in the season, when the weather is getting colder, can also hinder germination. The seeds may not have enough time to establish roots before winter arrives, making them vulnerable to frost damage.
How often should I water my new lawn?
It’s essential to water your new lawn consistently, especially during the first few weeks after planting. Aim for a light watering several times a day to keep the soil moist but not soggy.